Welcome to pyGenClean’s documentation!¶
Introduction¶
Genetic association studies making use of high throughput genotyping arrays need to process large amounts of data in the order of millions of markers per experiment. The first step of any analysis with genotyping arrays is typically the conduct of a thorough data clean up and quality control to remove poor quality genotypes and generate metrics to inform and select individuals for downstream statistical analysis.
pyGenClean is a bioinformatics tool to facilitate and standardize the
genetic data clean up pipeline with genotyping array data. In conjunction with
a source batch-queuing system, the tool minimizes data manipulation errors, it
accelerates the completion of the data clean up process and it provides
informative graphics and metrics to guide decision making for statistical
analysis.
pyGenClean is a command tool working on both Linux and Windows
operating systems. Its usage is shown below:
$ run_pyGenClean --help
usage: run_pyGenClean [-h] [-v] [--bfile FILE] [--tfile FILE] [--file FILE]
[--report-title TITLE] [--report-author AUTHOR]
[--report-number NUMBER]
[--report-background BACKGROUND] --conf FILE
Runs the data clean up (pyGenClean version 1.8.3).
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
Input File:
--bfile FILE The input file prefix (will find the plink binary
files by appending the prefix to the .bim, .bed and
.fam files, respectively).
--tfile FILE The input file prefix (will find the plink transposed
files by appending the prefix to the .tped and .tfam
files, respectively).
--file FILE The input file prefix (will find the plink files by
appending the prefix to the .ped and .fam files).
Report Options:
--report-title TITLE The report title. [default: Genetic Data Clean Up]
--report-author AUTHOR
The current project number. [default: pyGenClean]
--report-number NUMBER
The current project author. [default: Simple Project]
--report-background BACKGROUND
Text of file containing the background section of the
report.
Configuration File:
--conf FILE The parameter file for the data clean up.
The tool consists of multiple standalone scripts that are linked together via a
main script (run_pyGenClean) and a configuration file (the --conf
option), the latter facilitating user customization.
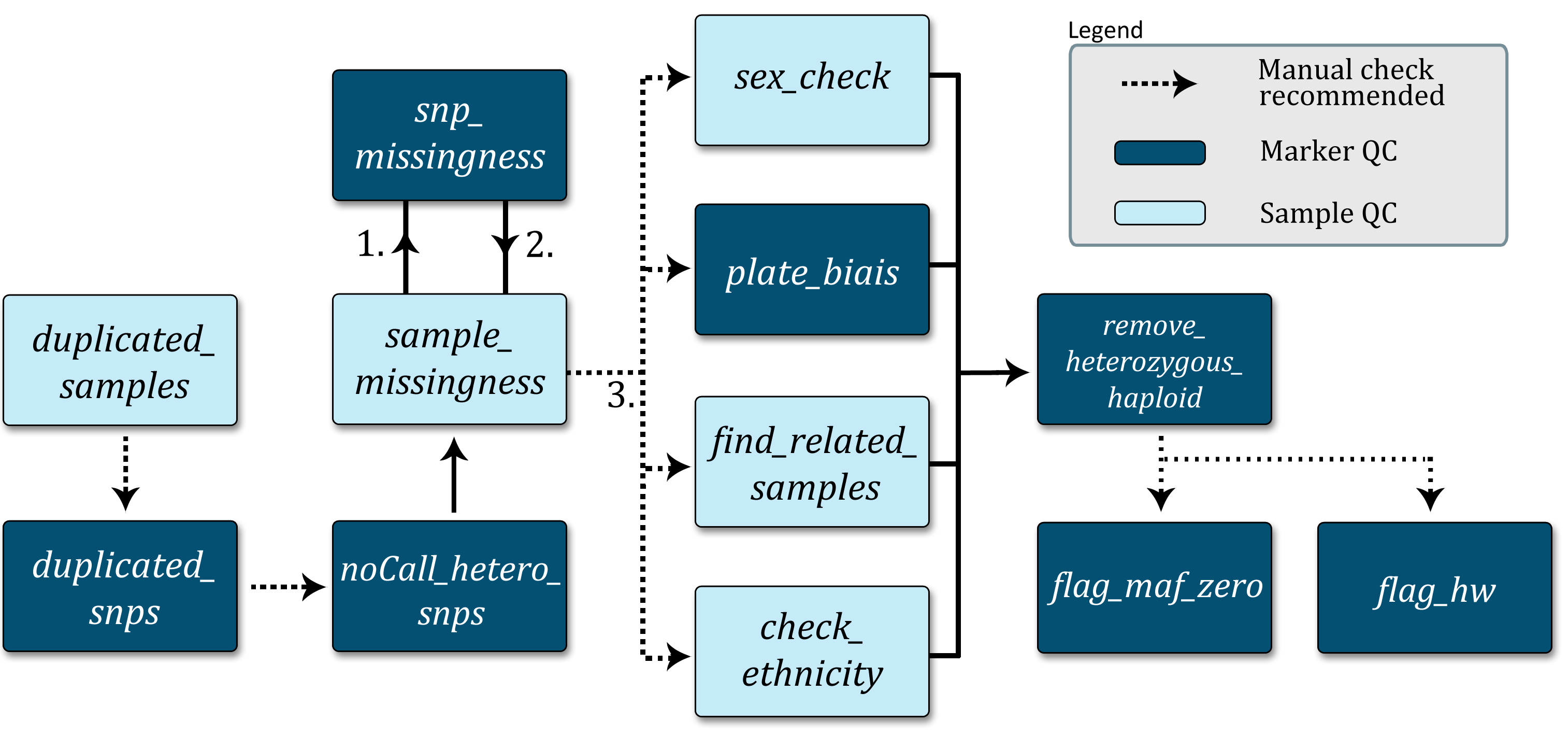
The Data clean up protocol schema shows the proposed data cleanup pipeline. Each box represents a customizable standalone script with a quick description of its function. Optional manual checks for go-no-go decisions are indicated.
Installation¶
pyGenClean is a Python package that works on both Linux and Windows
operating systems. It requires a set of Python dependencies and PLINK. Complete
installation procedures are available for both Linux (32 and 64 bits) and
Windows in the following sections.
Input files¶
To use pyGenClean, two sets of files are required: a set of genotype
files and a configuration file (using the
INI format).
Genotype files¶
The input files of the main program (run_pyGenClean) are either:
- PLINK’s pedfile format (use
pyGenClean‘s--fileoption) consists of two files with the following extensions:PEDandMAP. - PLINK’s transposed pedfile format (use
pyGenClean‘s--tfileoption) consists of two files with the following extensions:TPEDandTFAM. - PLINK’s binary pedfile format (use
pyGenClean‘s--bfileoption) consists of three files with the following extensions:BED,BIMandFAM.
For more information about these file formats, have a look at PLINK’s website, in the Basic usage/data formats section (http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink/data.shtml).
Warning
If the format used is the transposed one, the columns must be separated using tabulations, but alleles of each marker need to be separated by a single space.
To create this exact transposed pedfile format, you need to use the following PLINK’s options:
--recodeto recode the file.--transposedto create an output file in the transposed pedfile format.--tabto use tabulations.
Configuration file¶
To customized pyGenClean, a basic configuration file is required. It
tells which script to use in a specific order. It also sets the different
options and input files, so that the analysis is easy to replicate or modify.
The configuration file uses the INI format.
It consists of sections, led by a [section] header (contiguous integers
which gives the order of the pipeline) and followed by customization of this
particular part of the pipeline. Lines preceded by a # are comments and are
not read by pyGenClean.
The following example first removes samples with a missing rate of 10% and more
(section starting at line 1), then removes markers with a missing rate of
2% and more (section starting at line 6). Finally, it removes the samples
with a missing rate of 2% and more (section starting at line 3).
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | [1]
# Removes sample with a missing rate higher than 10%.
script = sample_missingness
mind = 0.1
[2]
# Removes markers with a missing rate higher than 2%.
script = snp_missingness
geno = 0.02
[3]
# Removes sample with a missing rate higher than 2%.
script = sample_missingness
mind = 0.02
|
For a more thorough example, complete configuration files are available for download at http://www.statgen.org and are explained in the Configuration Files section. For a list of available modules and standalone script, refer to the List of Modules and their Options.
Information about the protocol¶
The following sections describe the proposed protocol and provides information about which file should be looked for quality control. Finally, configuration files (with all available parameters) are given.
- Proposed Protocol
- Contamination Module
- Preprocessing Steps
- Duplicated Samples Module
- First Subset Module (optional)
- Duplicated Markers Module
- Second Subset Module (optional)
- Clean No Call and Only Heterozygous Markers Module
- Sample Missingness Module (mind 0.1)
- Marker Missingness Module
- Sample Missingness Module (mind 0.02)
- Sex Check Module
- Plate Bias Module
- Related Samples Module
- Ethnicity Module
- Third Subset Module
- Heterozygote Haploid Module
- Minor Allele Frequency of Zero Module
- Fourth Subset Module (optional)
- Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Module
- Fifth Subset Module (optional)
- Configuration Files
- How to Run the Pipeline
- Automatic Report
The algorithm¶
All the functions used for this project are shown and explained in the following section:
- Main pyGenClean pipeline
- Contamination Module
- Duplicated Samples Module
- Duplicated Markers Module
- Clean No Call and Only Heterozygous Markers Module
- Sample Missingness Module
- Marker Missingness Module
- Sex Check Module
- Plate Bias Module
- Heterozygous Haploid Module
- Related Samples Module
- Ethnicity Module
- Minor Allele Frequency of Zero Module
- Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium Module
- Comparison with a Gold Standard Module
- Plink Utils
Citing pyGenClean¶
If you use pyGenClean in any published work, please cite the
published scientific paper describing the tool.
Lemieux Perreault LP, Provost S, Legault MA, Barhdadi A, Dubé MP: pyGenClean: efficient tool for genetic data clean up before association testing. Bioinformatics 2013, 29(13):1704-1705 [DOI:10.1093/bioinformatics/btt261]